Press Releases
Note: Click on the header titles below to expand or collapse an accordion panel.
-
 Novel Protective Antibody Target Against Crimean Congo Hemorrhagic Fever Virus Identified (28-Feb)
Novel Protective Antibody Target Against Crimean Congo Hemorrhagic Fever Virus Identified (28-Feb)
A research team led by the United States Army Medical Research Institute of Infectious Diseases, has discovered an important protective antibody target against Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever virus, or CCHFV. Their work, which appears online today in the journal Nature Communications, could lead to the development of protective antibodies for infected patients. Continue Reading »
-
 USAMRIID to Hold Change of Command Ceremony June 22 at Fort Detrick (21-Jun)
USAMRIID to Hold Change of Command Ceremony June 22 at Fort Detrick (21-Jun)
COL Aaron C. Pitney will assume command of the U.S. Army Medical Research Institute of Infectious Diseases in a ceremony at Fort Detrick June 22 at 10:00 a.m. He succeeds COL Constance L. Jenkins, who has headed the Institute since June 2021 and will become the Special Assistant to The Surgeon General for Military Health System Governance, Falls Church, Va. Continue Reading » -
 USAMRIID Scientist Arthur M. Friedlander Elected to American Academy of Microbiology (7-Mar)
USAMRIID Scientist Arthur M. Friedlander Elected to American Academy of Microbiology (7-Mar)
Arthur M. Friedlander, M.D., senior scientist at the U.S. Army Medical Research Institute of Infectious Diseases, has been elected Fellow of the American Academy of Microbiology. He is one of 65 members to be recognized in 2023. Continue Reading » -
 Dr. Joel Bozue Named USAMRIID Civilian of the Quarter (11-Jan)
Dr. Joel Bozue Named USAMRIID Civilian of the Quarter (11-Jan)
Dr. Joel Bozue was named Civilian of the Quarter (Q3) at the U.S. Army Medical Research Institute of Infectious Diseases (USAMRIID) at Fort Detrick, Md. Bozue, a principal investigator in the Institute's Bacteriology Division, served as the U.S. Chairman of the Medical Biological Defense Working Group for the 20th Shoresh Conference on Military Medicine held in September 2022. Continue Reading » -
 USAMRIID Focuses on Genome Sequencing to Detect Variants (5-Jan)
USAMRIID Focuses on Genome Sequencing to Detect Variants (5-Jan)
The U.S. Army Medical Research Institute of Infectious Diseases's Center for Genome Sciences played a key role in support during the COVID-19 pandemic. Continue Reading »
-
 U.S. Army medical team helps Smithsonian National Zoo to protect endangered Red Pandas (13-Dec)
U.S. Army medical team helps Smithsonian National Zoo to protect endangered Red Pandas (13-Dec)
A U.S. Army medical team contributed to an investigation into the cause of death of a Red Panda at the Smithsonian's National Zoo and Conservation Biology Institute (NZCBI). Continue Reading » -
 Researchers Detect Monkeypox Virus in Testes of Nonhuman Primate Survivors (17-Oct)
Researchers Detect Monkeypox Virus in Testes of Nonhuman Primate Survivors (17-Oct)
For the first time, scientists have detected monkeypox virus in the testes of macaques during the acute phase of infection, according to research published online today in the journal Nature Microbiology. In addition, the team found preliminary evidence of persistent infection in two animals that survived challenge with the virus. Their results highlight the potential for sexual transmission of the virus in humans. Continue Reading » -
 Messenger RNA Technology Could Be Used to Develop Infectious Disease Therapeutics (7-Jul)
Messenger RNA Technology Could Be Used to Develop Infectious Disease Therapeutics (7-Jul)
Army scientists and industry partners were among the first to demonstrate that messenger RNA (mRNA)–the technology recently used in COVID-19 vaccines and others–could also be used to develop treatments for infectious diseases. Their work appears in the June 2022 issue of the journal Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids, published by Cell Press. Continue Reading » -
 Research Sheds Light on Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever Disease Process (20-May)
Research Sheds Light on Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever Disease Process (20-May)
Army scientists determined that the body's own natural immune response contributes to disease severity in mice infected with Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus (CCHFV), which causes a widespread tick-borne viral infection in humans. Their work, published in today's edition of PLOS Pathogens, provides a deeper understanding of how the virus causes disease and forms a basis for developing medical countermeasures to prevent and treat infection. Continue Reading » -
 Antibody Shows Promise for Developing Hantavirus Treatment (21-Mar)
Antibody Shows Promise for Developing Hantavirus Treatment (21-Mar)
An international research team discovered the first human antibody to effectively neutralize two types of hantaviruses in animal models, according to a study published online Mar. 16 in Science Translational Medicine. Based on their initial results, the antibody appears to be a promising candidate for developing a "pan-hantavirus" therapy to protect against outbreaks caused by multiple types of known or emerging hantaviruses. Continue Reading » -
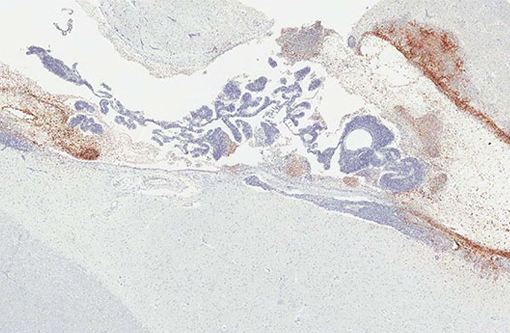 Study Reveals Ebola Virus Can Hide in Brain, Persist Even After Treatment (9-Feb)
Study Reveals Ebola Virus Can Hide in Brain, Persist Even After Treatment (9-Feb)
In a groundbreaking study published today, scientists describe how Ebola virus, which can persist in certain areas of the body, can re-emerge to cause fatal disease–even long after treatment with monoclonal antibodies. Their research, using a nonhuman primate model of Ebola virus infection, appears on the cover of today's edition of Science Translational Medicine. Continue Reading » -
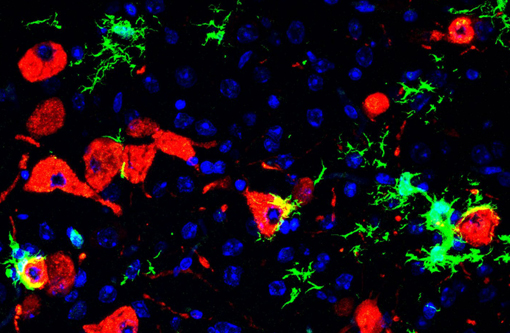 Scientists Develop First Lethal Hamster Model for COVID-19 (25-Jan)
Scientists Develop First Lethal Hamster Model for COVID-19 (25-Jan)
Army scientists, in collaboration with Utah State University, have developed a lethal hamster model for SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. This model system will aid in understanding the severe disease course of COVID-19–including the virus's interaction with the central nervous system–and will support the advancement of vaccines and therapeutics targeting the virus. Continue Reading »
-
 Experimental Treatment with Enzyme Protects Mice from Lethal Anthrax Infection (8-Dec)
Experimental Treatment with Enzyme Protects Mice from Lethal Anthrax Infection (8-Dec)
Scientists have demonstrated that modifying an enzyme produced by the bacterium that causes anthrax can protect mice from infection with the deadly disease. Their findings, published in today's online edition of Science Translational Medicine, suggest a potential therapeutic strategy for treating multidrug-resistant strains of anthrax, and could lead to new treatments for other bacterial infections. Continue Reading » -
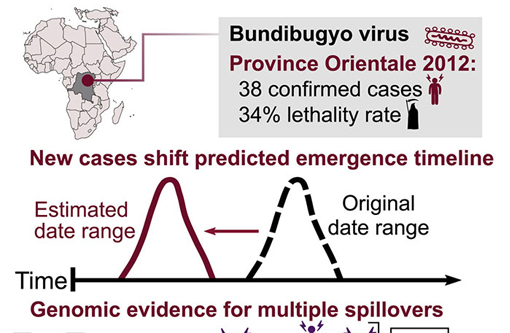 Gene Sequencing Tools Pinpoint Origins of Bundibugyo Virus Disease Outbreak (28-Jul)
Gene Sequencing Tools Pinpoint Origins of Bundibugyo Virus Disease Outbreak (28-Jul)
New research sheds light on the origins of a 2012 Bundibugyo virus disease outbreak in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, according to a report published online this week in the journal Cell Reports Medicine. The work also demonstrates the importance of using high throughput sequencing to understand virus "spillover" events in order to more effectively manage disease outbreaks. Continue Reading »
-
Scientists Develop Novel Therapy for Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever Virus (1-Jun)
Army scientists working as part of an international consortium have developed and tested an antibody-based therapy to treat Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus (CCHFV), which is carried by ticks and kills up to 60 percent of those infected. Their results are published online today in the journal Cell. Continue Reading » -
Scientists Establish Multiple Primate Models of SARS-CoV-2 Airborne Infection (4-Feb)
Army scientists evaluated three nonhuman primate species as potential models of SARS-CoV-2 airborne infection, according to results published online this week in PLOS ONE. Their work demonstrates that any of these species may be useful for testing vaccines and therapies in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, which has resulted in over 104 million cases and more than 2 million deaths worldwide in the past year. Continue Reading »
Last Modified Date: 28-Feb-2024
 An official website of the United States government
An official website of the United States government
 ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .mil website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .mil website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
